More and more young adults are relying on the Bank of Mom and Dad. For perhaps the first time in US history, today’s 30 year old faces a tougher time than their parents did. Today’s young adults may be worse off than their parents were at age 30. And it’s not because of laziness. It has gotten harder for young people to reach the same milestones as their parents.
Thirty years ago, the average house price in the US was $154,200. Today, it is $501,700. The average private university tuition was $11,481, 30 years ago. Today, my Alma Mater, Oberlin College charges $66,410 for tuition alone and has a total annual cost of $86,800. Many of my classmates pursued a 5-year double degree program, which today will probably cost over $450,000.
Wages in many careers have not kept pace with inflation. Students are encouraged to go to the best college possible and to pursue advanced degrees, racking up massive student debt. 45% of student loans are on an income driven repayment plan, and over one million Americans have so little income that they qualify for a $0 monthly payment on their federal students loans. Of course, the interest still accrues and they cannot discharge student loans in bankruptcy.
The cost of healthcare has risen more than inflation and child care expenses have made it difficult for parents. Many have calculated that after-tax, they are better off having one parent stay home.
I think the Wealth Inequality in America is likely to widen rather than shrink for the decades ahead. Who will come out ahead? Adults from wealthy families will likely stay ahead of young adults from less privileged backgrounds. We would like to think that America is a meritocracy, but it is becoming harder for young people to create their own economic security. 70-year old millionaires can lecture young people about hard work, but it’s not in touch with the reality of the times.
I’ll leave it to Washington to solve the nation’s problems, but I doubt that solutions will be coming soon. I think parents are going to have to look out for their kids more and for longer than just getting them to age 18 or 22. Parents will have a role in making sure their children become wealthy. We can only take care of our own family, so let’s start there.
This does not mean setting up a massive Trust Fund so that your kids don’t have to earn a living. No, parents don’t want their kids to become dependent on their generosity. We don’t want to create the moral hazard that they would fail to pursue their own career to the fullest. But there are ways that The Bank of Mom and Dad can help establish your child’s financial success, security, and stability.
The Good News
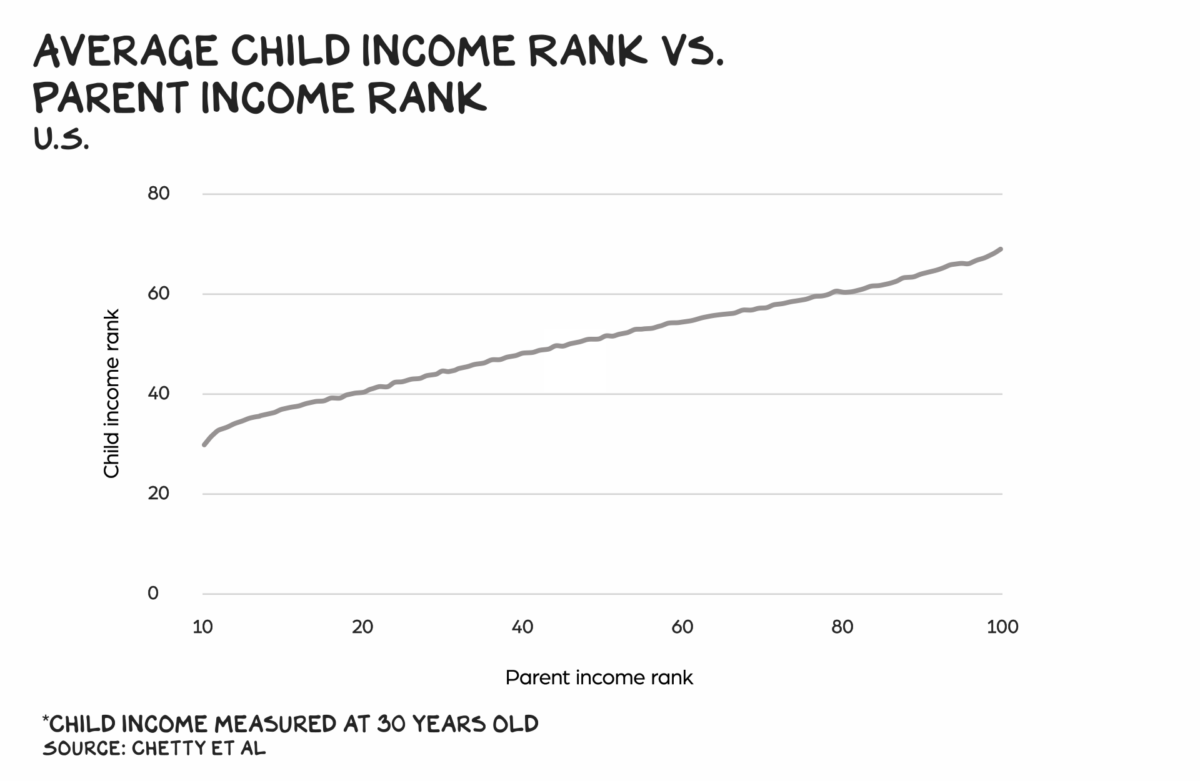
The good news is that wealthy parents tend to have wealthy children. At age 30, children’s income is highly correlated to their parent’s income. Children may not listen to what you say, but they often make similar decisions as their parents, including in their careers.
Minimizing Student Loans
Here is an important rule of thumb for college students. Keep your total student loans to no more than one-time (1X) your future salary. Entering a career with a $50,000 salary? Your student loans should be $50,000 or less to allow you to repay over the standard 10-year schedule. And only a surgeon making $350,000 a year should ever consider having $350,000 in student loans. But I have seen people with incomes under $100k with that level of student debt.
Here’s some advice for parents:
- Make sure your kids are thinking about the 1X rule and choosing a college which will not cripple them with future debt. It’s okay for your children to have some skin in the game and have to pay or borrow a little for college. But don’t let them be foolish and invest $500,000 into a field that will only pay $50,000 a year. Debt is not the path to economic security.
- Start saving earlier in a 529 Plan or be willing and able to absorb more of the college costs at the time they are in school.
- Aim to have them go into a field with 90% plus employment. There are great careers which are highly in demand and offer a terrific salary. Are there jobs which will have this exact degree as a pre-requisite? Seek degrees with value.
- After college, help your kids be mobile. In their 20’s, it is the time to pursue a career and go where that takes them. If the great jobs are on Wall Street, Silicon Valley, or wherever, that flexibility gives them a leg-up versus older job candidates who are unwilling to move. My wife’s company has promoted her four times, including most recently to Paris. This is how you build a career in 2024, not by going back home and living in the same town as your parents.
Fund Their Roth IRAs
I got my first job at age 16 at the minimum wage of $3.35 an hour. I worked at the Long Point amusement park for about four weeks before it burned down from an electrical short. The owner didn’t have insurance and that was the end of the 80 year old park – and my first job. I do think having a part time job is a great learning experience and can help young people develop important skills.
Anyone who has earned income can fund a Roth IRA, including someone who is 16 or younger. What I would suggest parents do is allow your kids to keep their income while the parents fund their children’s Roth IRAs. You will give them a tremendous advantage in their future wealth by getting this early start. You can invest up to $7,000 a year, or the level of their annual income, whichever is lower.
Let’s say you fund a Roth IRA for your son or daughter for $5,000 for 10 years from age 16 through 25. We invest in an Index Fund and earn 7% per year. By the time they are age 66, they would have $1,181,000 in their tax-free account, all thanks to Mom and Dad funding a Roth IRA for their first 10 years of part-time work. That’s the power of compound interest.
Annual Gift Exclusion
If you have enough in resources to know that your retirement is secure and you will have more than enough, then you may want to start giving away some money during your lifetime to your children. The annual gift tax exclusion for 2024 is $18,000 per person. You can give that amount to each child and a married couple can double that, to $36,000 per child per year.
Every article seems to get this wrong: If you give away more than the annual exclusion you don’t immediately owe a gift tax. But you must file a gift tax return and the amount above the exclusion will reduce your lifetime unified estate/gift exemption. For 2024 that amount is $13.61 million and again it is double for a married couple. Most parents are going to be below the lifetime exemption amount and could give away more. But, the easiest first step is to use the full $18,000 annual exclusion.
This could be a great way to gradually create an account which your adult children could use as a house down payment, or to start a business, or pursue extra career development. This account could also serve to teach them about long-term investing, the benefits of index funds, and planning for goals.
Housing and Living Expenses
Certainly a lot of parents are helping their young adults with housing, a car, health insurance, cell phones, etc. Hopefully, this will allow them to focus on developing their long-term career and avoid going into debt. In a lot of expensive areas, kids are returning home to live with their parents after college. This can help them pay down their student loans faster. And with rents having gone up so much since 2019, this seems to be becoming more and more common.
What about buying a duplex for your child to House Hack? There are lots of creative ways to help your children with expenses. The goal is to have them get started investing and be able to save aggressively or pay down debt faster.
Managing The Bank of Mom and Dad
No One Is Self-Made. We have all benefited from the Education system in America, as well as the laws and regulations which promote free trade and protect employee rights. Compared to the rest of the world, the US remains a great place to become an entrepreneur or highly paid professional. We shouldn’t forget the unique opportunities we have to find economic security in the US. But even with all the benefits, the fact remains that parents have a very large role to play.
It is getting harder for today’s young adults. Inflation is a problem for housing, college tuition, health care, and starting a family. Those costs have grown much faster than incomes. As a result, young adults are falling behind previous generations. The Bank of Mom and Dad can help with planning, wisdom, and yes, sometimes with more money. Nearly half of all first-time homebuyers under age 35 have had some family assistance with their purchase.
Hopefully, well-to-do parents are already thinking about how they can create inter-generational wealth. What are the most effective ways and times to be giving money to your kids? What can go wrong or what are some unintended consequences? How do you treat two or three kids with different needs and abilities to handle the money? These are not easy decisions or conversations. But they are vital discussions to be having as a family, and yes, with your financial planner, too.
We can help you determine what you can truly afford and think about how to best help children with your financial support. We have a number of families where we work with the parents and with their children in their twenties and thirties. Wealth is a habit, and financial planning is a skill. Being good with money is not a skill which is being taught in school, unfortunately. But parents do have a role in talking about money, and even more importantly, modelling the behavior and generosity which you hope to instill in your children.








